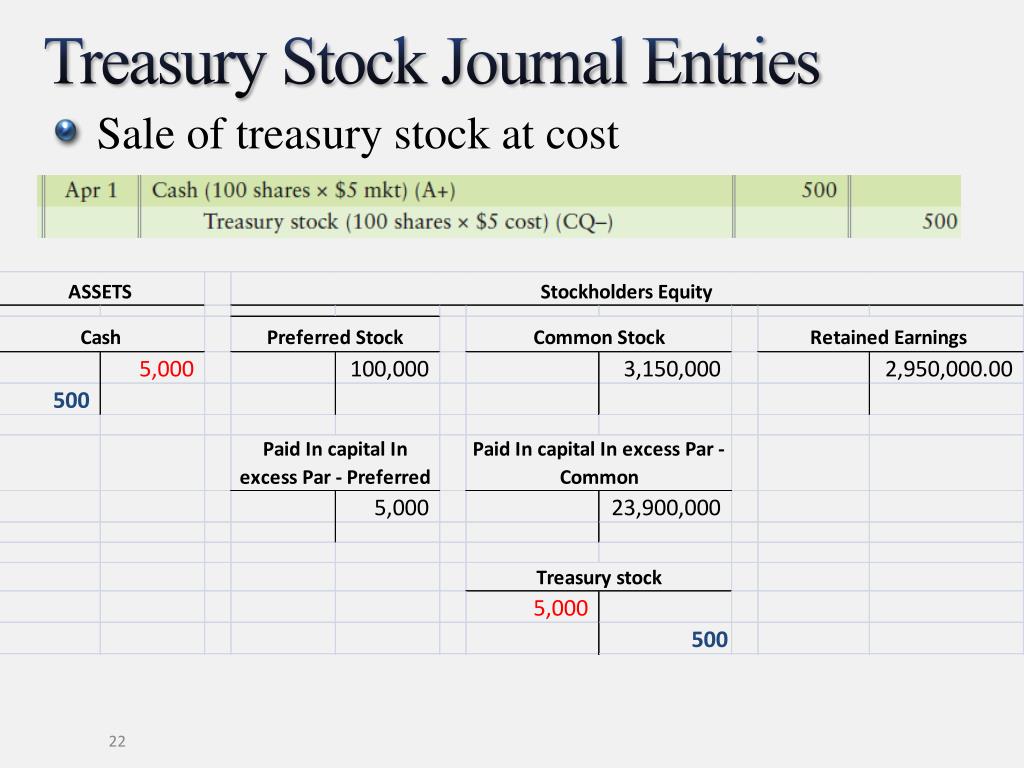
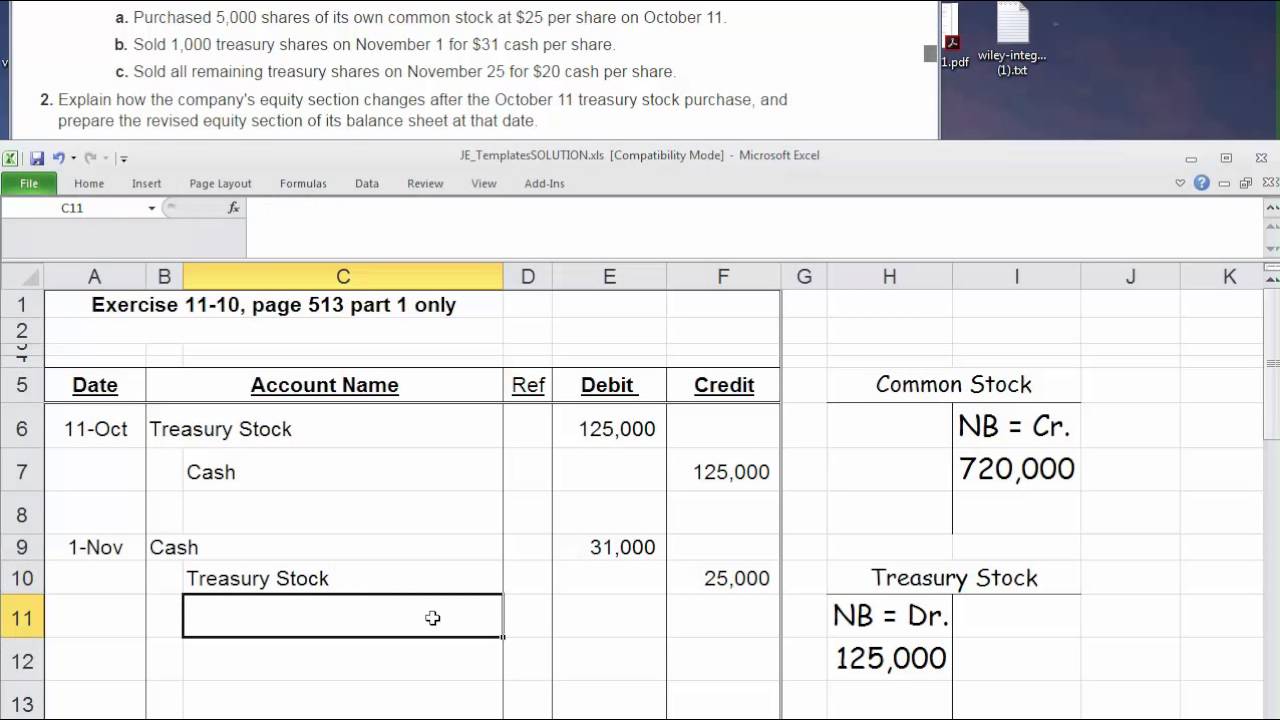
Selling Treasury Stock Journal Entry - Web journal entry for reissuing treasury stock. They are two methods of recording these stocks: Web the entries to record these events are: The original cost paid for each treasury share, $25, is multiplied by the 100 shares to be resold, or $2,500. Web how to record treasury stock. (shares issued x price paid per share) or market value of item received. Web the following journal entry is recorded for the purchase of the treasury stock under the cost method. Under the cost method, if the treasury stock is purchased, the following entry is passed with the actual amount of purchase. Web the journal entry for selling treasury stock is a debit to the cash account for the proceeds received and a credit to the treasury stock account for the amount of the sale. The journal entry to record this sale of the treasury shares at cost is:
Journalizing Treasury Stock Transactions (Cost Method) YouTube
Web in this journal entry of the sale of treasury stock, both total assets and total equity in the balance sheet increase by $75,000. The.
PPT Corporations Effects on Retained Earnings and the
Entries for stock without par value par value method of treasury stock faqs. Web in this journal entry of the sale of treasury stock, both.
Treasury Stock Journal Entries Exercise YouTube
Even though the company is purchasing stock, there is no asset recognized for the purchase. 1.6k views 8 years ago. (shares issued x par value).
Example of Treasury Stock sold Below Cost YouTube
Web updated on april 29, 2023. The par value method is based on the assumption that the acquisition of treasury stock is essentially a permanent.
Treasury Stock Journal Entries YouTube
Web the following journal entry is recorded for the purchase of the treasury stock under the cost method. Web the following journal entry is recorded.
Treasury Stock Journal Entries YouTube
1.6k views 8 years ago. Last updated october 26, 2022. An entity cannot own part of itself, so no asset is acquired. Imagine a company.
Treasury Stock Example and Treasury Stock Journal Entry
Last updated october 26, 2022. Even though the company is purchasing stock, there is no asset recognized for the purchase. They are two methods of.
Problem 132A Treasury Stock Journal Entries (part a) YouTube
Treasury stock balance sheet accounting. Web to record the issue of common (or preferred) stock, you will: Web the journal entry for selling treasury stock.
Buying & Selling Treasury Stock (Journal Entries) YouTube
Even though the company is purchasing stock, there is no asset recognized for the purchase. The par value method is based on the assumption that.
Even Though The Company Is Purchasing Stock, There Is No Asset Recognized For The Purchase.
1.6k views 8 years ago. An entity cannot own part of itself, so no asset is acquired. Web the journal entry to record this sale of the treasury shares at cost is: Treasury stock balance sheet accounting.
Under The Cost Method, If The Treasury Stock Is Purchased, The Following Entry Is Passed With The Actual Amount Of Purchase.
This transaction will reduce the amount of treasury stock held by the company. Web how to record treasury stock. Web in the journal entry, the controller is eliminating the $100,000 originally credited to the common stock account and associated with its par value. Web to record the issue of common (or preferred) stock, you will:
Web Journal Entry For Reissuing Treasury Stock.
Last updated october 26, 2022. Web the journal entry for selling treasury stock is a debit to the cash account for the proceeds received and a credit to the treasury stock account for the amount of the sale. Web the following journal entry is recorded for the purchase of the treasury stock under the cost method. This account, however, never develops a debit balance.
Web If Soccer Trio Corporation Sells The Remaining 7,500 Shares Of Its Treasury Stock For $21, The Entry To Record The Sale Would Be As Shown:
They are two methods of recording these stocks: The cost method ignores the par value of the share of the company. Web sale at more than cost: An entity cannot own part of itself, so no asset is acquired.