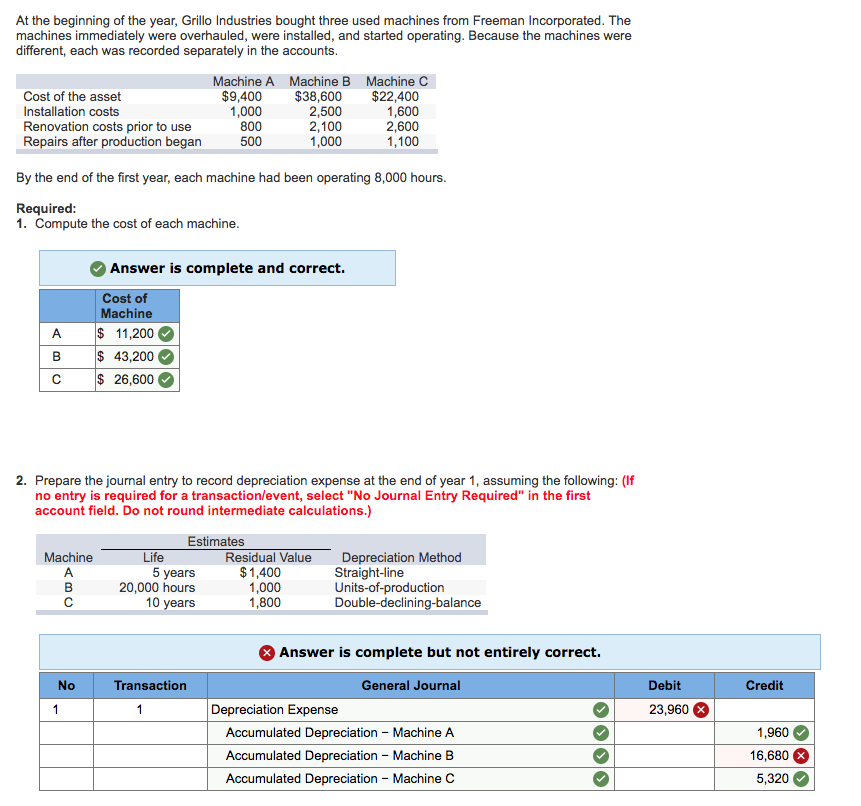
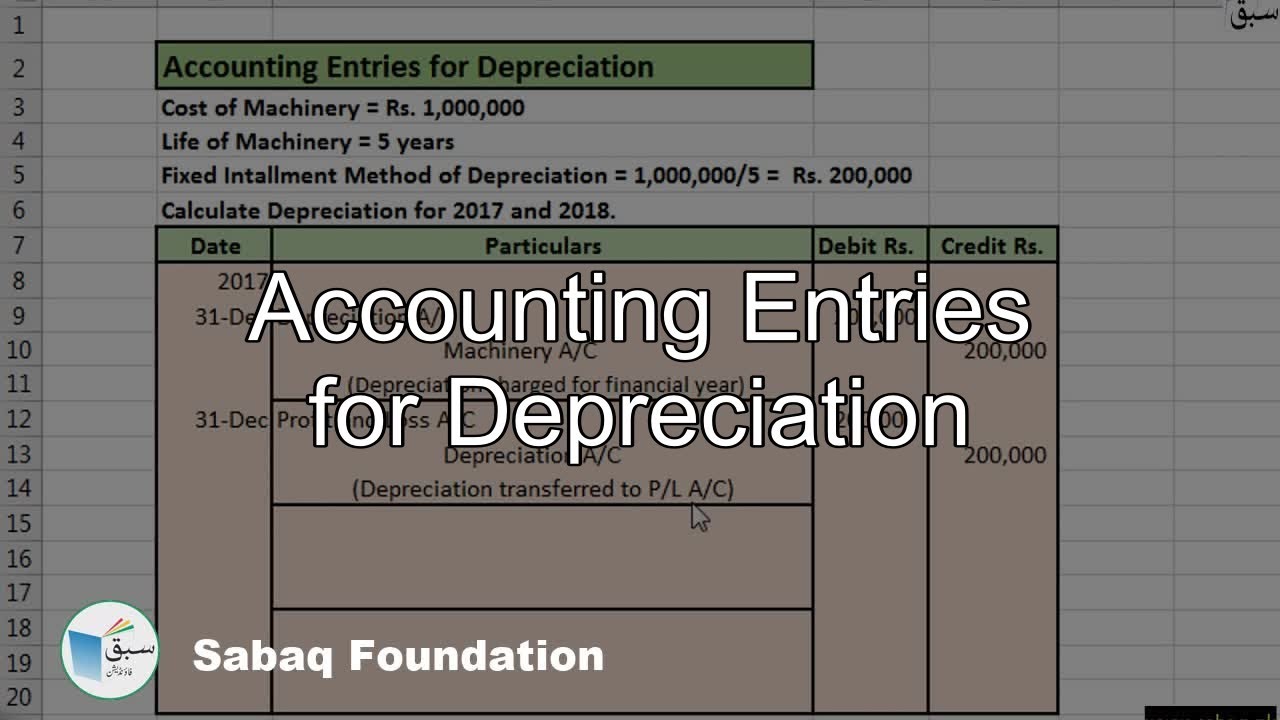
Recording Depreciation Journal Entry - We simply record the depreciation on debit and credit to accumulated depreciation. See the basic and detailed journal entries for depreciation, and the cash impact and capitalization limit. Web depreciation is recorded by debiting depreciation expense and crediting accumulated depreciation. Web also, record the journal entries. Web construct the journal entry to record the disposal of property or equipment and the recognition of a gain or loss. This is recorded at the end of the period (usually, at the end of every month, quarter, or year). This method spreads the depreciation cost evenly over the useful life of an asset. $0.09 × 30,000 = $2,700. Credit the fixed asset account for the original cost of the asset. Once depreciation has been calculated, you’ll need to record the expense as a journal entry.
Solved Prepare the journal entry to record depreciation
Credit to the balance sheet account accumulated depreciation. Once depreciation has been calculated, you’ll need to record the expense as a journal entry. Web at.
Depreciation and Disposal of Fixed Assets Finance Strategists
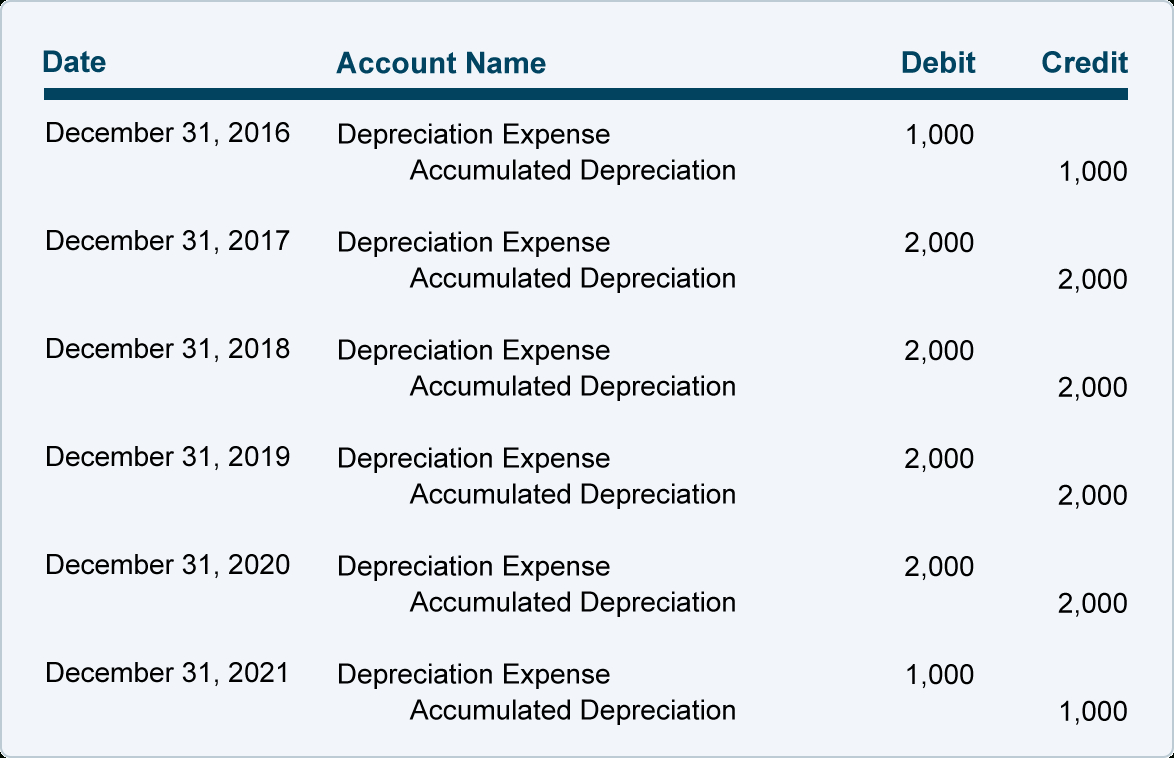
This is recorded at the end of the period (usually, at the end of every month, quarter, or year). The entry to record the $6,000.
Recording Depreciation Expense for a Partial Year
Debit the accumulated depreciation account for the amount of depreciation claimed over the life of the asset. The entry to record the same is as.
Depreciation Explanation Accountingcoach with Bookkeeping Reports
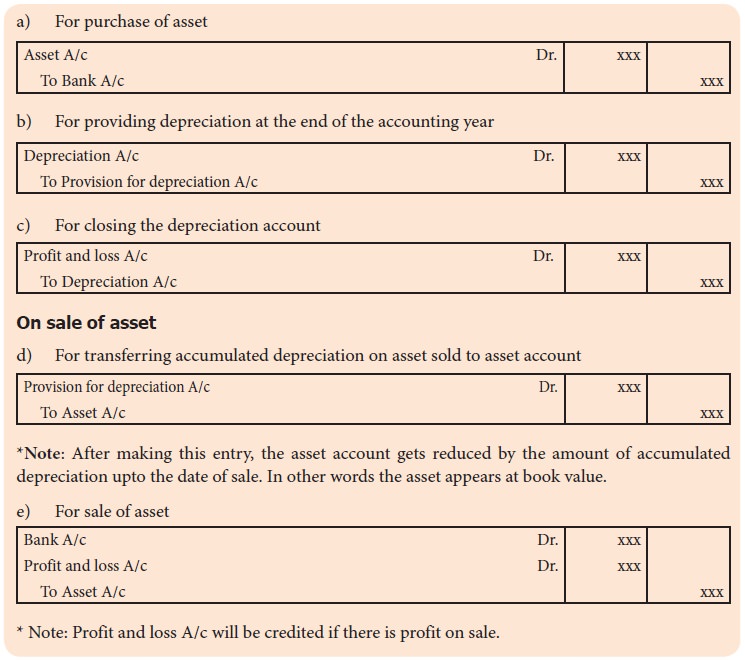
Where xxx is the amount of depreciation for the period. The primary objective behind these adjustments is to transition from cash transactions to the accrual..
Methods of recording depreciation Accountancy
$0.09 × 20,000 = $1,800. Web the entry to record accumulated depreciation is as below: Web to record a depreciation journal entry, businesses need to.
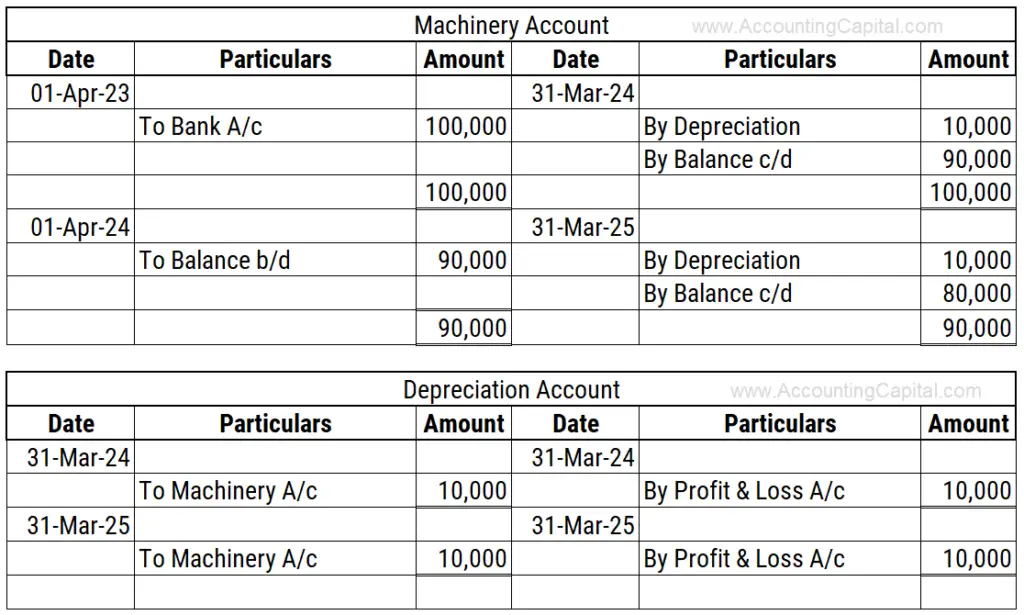
Depreciation & Accumulated Depreciation Journal Entry and Balance Sheet
Web straight line depreciation journal entry. Where xxx is the amount of depreciation for the period. Web depreciation journal entry example: From the view of.
What is the journal entry for depreciation? Leia aqui What is
Depreciation is the gradual charging to expense of an asset’s cost over its expected useful life. The depreciable basis of an asset includes all the.
Depreciation Journal Entry With Example Howto Diy Today
Therefore, it is very important to understand that when a depreciation expense journal entry is recognized in the. This is recorded at the end of.
Journal Entry for Depreciation Example Quiz More..
Therefore, it is very important to understand that when a depreciation expense journal entry is recognized in the. Credit the fixed asset account for the.
Web The Journal Entry For Depreciation Is:
Debit the cash account for the proceeds from the. Credit to the balance sheet account accumulated depreciation. Once the annual depreciation expense has been calculated, incorporating both tangible and intangible assets, they can proceed to record the journal entry. Once depreciation has been calculated, you’ll need to record the expense as a journal entry.
The Entry To Record The Same Is As Follows:
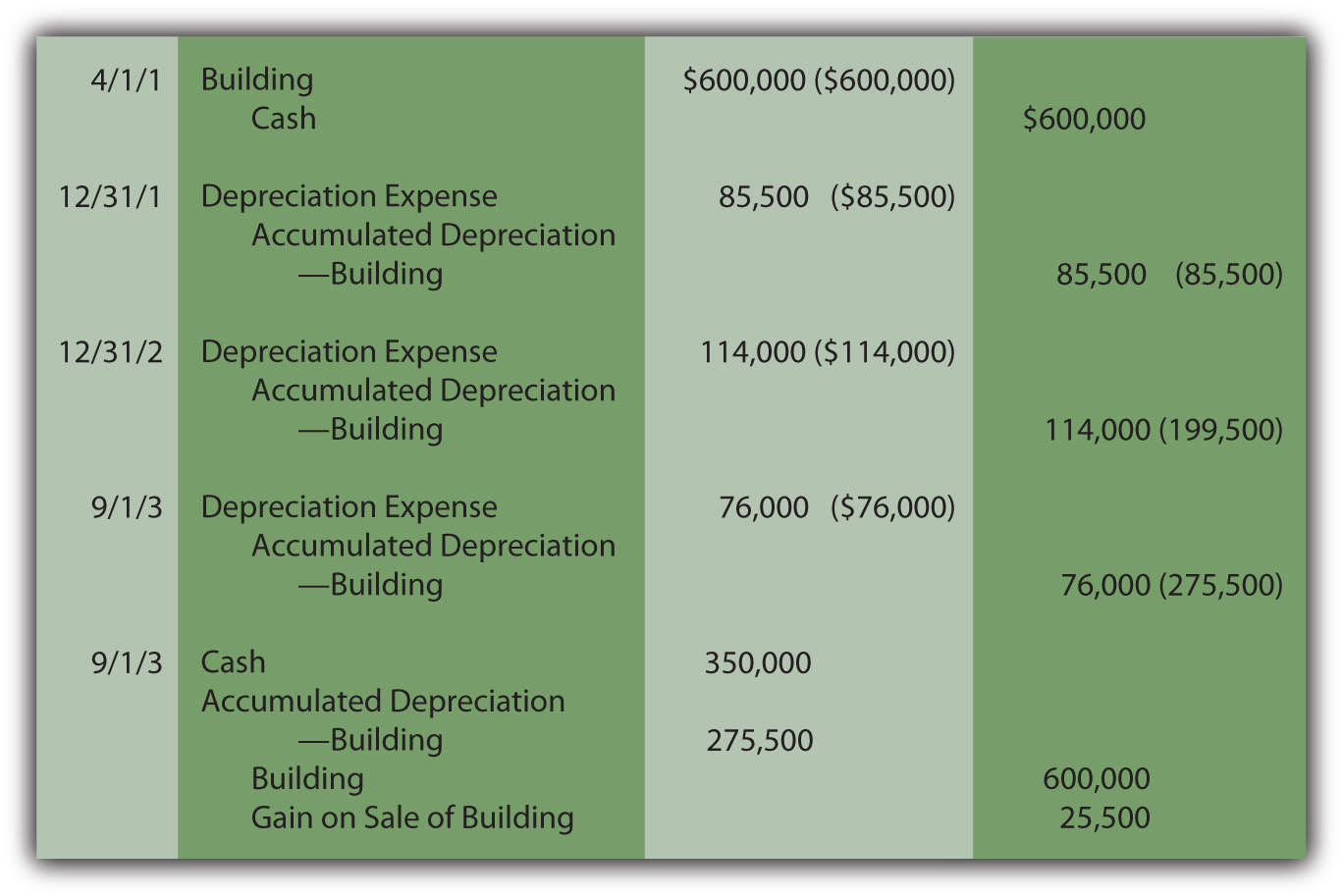
Life cycle of an asset. Web depreciation journal entry example: Web a depreciation journal entry is used at the end of each period to record the fixed asset or plant asset depreciation in the accounting system. The entry to record the $6,000 depreciation every year would be:
At The End Of Useful Life, The Net Book Value Of The Asset.
This is recorded at the end of the period (usually, at the end of every month, quarter, or year). In this case, we can make the journal entry of depreciation expenses in the june 30 adjusting entry as below: Credit the fixed asset account for the original cost of the asset. This journal entry is necessary for the company to present an actual net book value of its total assets as well as a more realistic view of its profit in june 2020.
It Considers The Total Years As The Useful Period And Divides The Value Of The Asset Minus Any Salvage Value Equally.
Accelerated depreciation methods, on the other hand, allocate a larger portion of the cost of the asset in the early years of its useful life and a smaller portion in later years. There are different methods of calculating depreciation, depending on the nature of the asset and the preference of the business. This method spreads the depreciation cost evenly over the useful life of an asset. $0.09 × 30,000 = $2,700.