Interest Receivable Journal Entry - Interest receivable is an asset that arises when a company. To the payee of the note, or lender, interest is. To the maker of the note, or borrower, interest is an expense; Web learn how to record interest receivable and interest income in the books of accounts with examples and explanations. Web learn how to record interest income and receivable in the accounting period with journal entries. Web interest income journal entry is crediting the interest income under the income account in the income statement and debiting the interest receivable account in the balance sheet. This entry typically involves two accounts: Web the process of recording interest receivable in financial accounting involves creating journal entries that reflect the accrued interest income. Web interest receivable is the amount of interest that a business has earned but has not yet been received in cash. The entry will reverse the accrued interest receivable from balance sheet.
Accrue Interest Receivable YouTube
Accrued interest journal entry example (debit, credit) expand +. Web interest income journal entry is crediting the interest income under the income account in the.
How to Record Interest Receivable Journal Entry? (Example, Definition
Web interest receivable is the amount of interest that a business has earned but has not yet been received in cash. Web the usual journal.
What is Accrued Interest? Formula + Loan Calculator
See the accounting treatment, the balance sheet position, and the. Web interest income journal entry is crediting the interest income under the income account in.
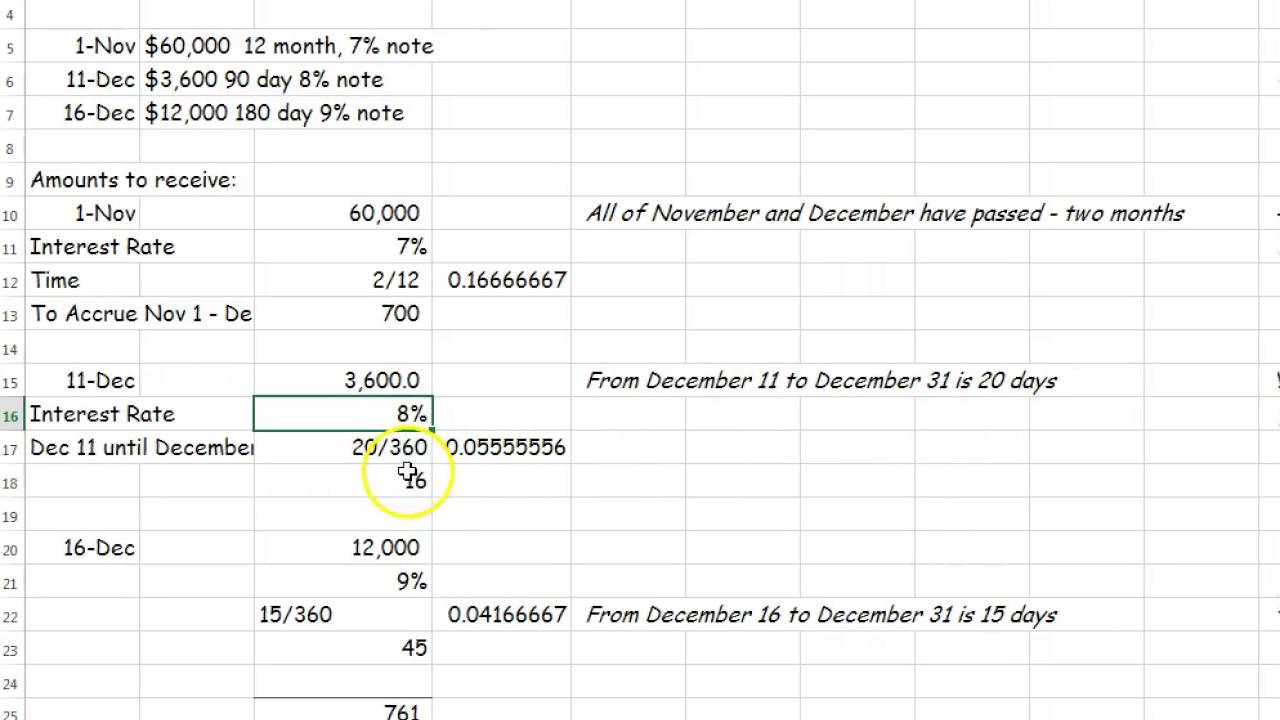
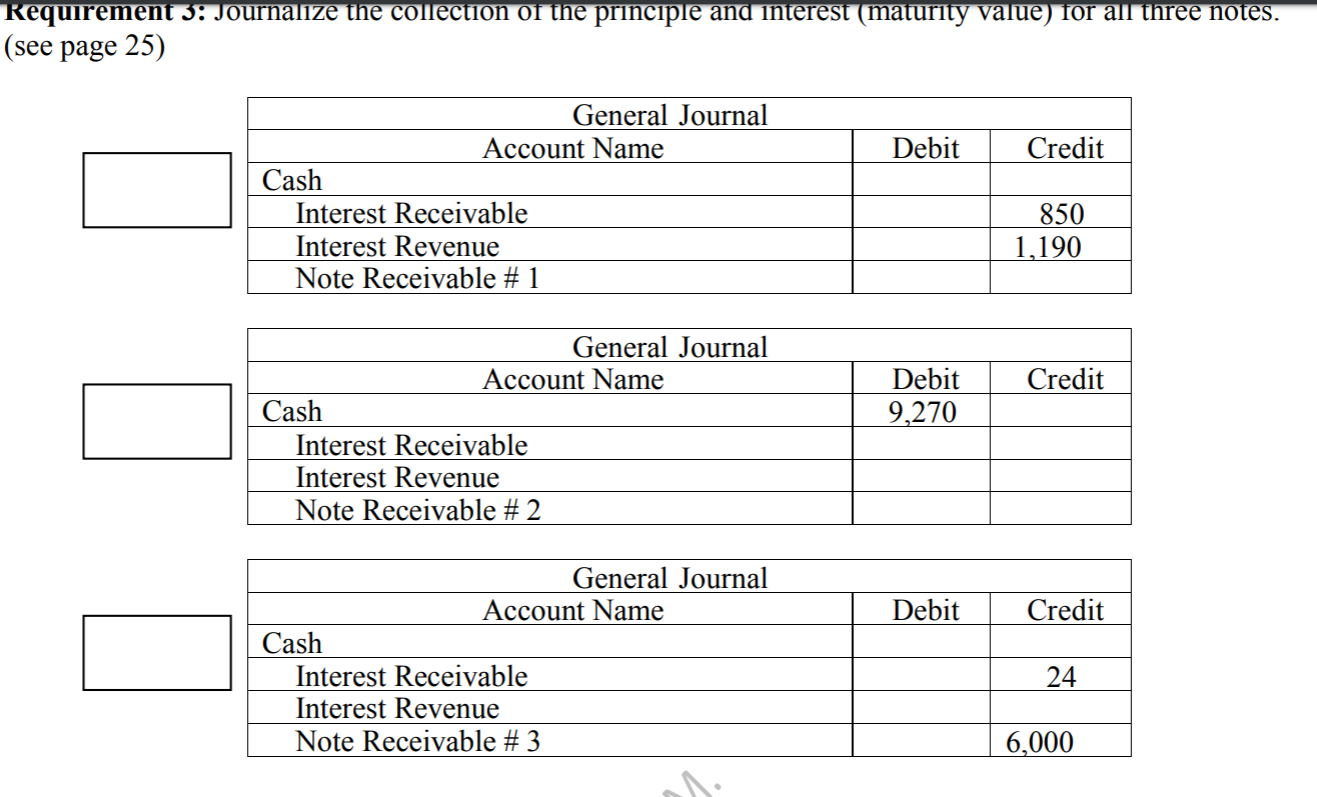
Outline page 28, the journal entry for the collection
Since the payment of accrued. Web the bank transaction journal entries below act as a quick reference, and set out the most commonly encountered situations.
Interest Receivable Journal Entry
See the debit and credit accounts, the accounting equation and an example of accrued interest. See examples of interest receivable journal entry for various scenarios.
What Is The Journal Entry For Receiving A Loan
Since the payment of accrued. Web interest is the fee charged for use of money over a specific time period. The entry will reverse the.
Adjusting Entries Adjusting Entries Interest Receivable
Web the usual journal entry used to record interest receivable is a debit to the interest receivable account and a credit to the interest income.
Journal Entries and Trial Balance in Accounting Video & Lesson
Since the payment of accrued. Web interest income journal entry is crediting the interest income under the income account in the income statement and debiting.
Notes Receivable Journal Entries, with Interest YouTube
Web $10,000 x 9% x 21 days/360 = $52.50. Introduction to the present value of a single amount (pv), calculations for the present value of.
See Examples Of Interest Receivable Journal Entry For Various Scenarios And Their Accounting Implications.
Web in the journal entry, interest receivable has a debit of $140. Web learn how to record interest receivable and interest revenue in accounting with journal entries and examples. The entry will reverse the accrued interest receivable from balance sheet. Web learn how to record interest receivable and interest income in the books of accounts with examples and explanations.
To The Maker Of The Note, Or Borrower, Interest Is An Expense;
Web the accounts receivable journal entries below act as a quick reference, and set out the most commonly encountered situations when dealing with the double entry posting of. Web an interest receivable journal entry in finance refers to the record made in the company’s general ledger that denotes the amount of interest that’s been earned but has. See the debit and credit accounts, the accounting equation and an example of accrued interest. Web $10,000 x 9% x 21 days/360 = $52.50.
Web Interest Is The Fee Charged For Use Of Money Over A Specific Time Period.
See an example of a fixed deposit with monthly interest and the journal entries. Web learn how to record interest receivable in different situations, such as bank deposits, loans, and bonds, with step by step journal entries and calculations. See when and how to adjust interest receivable at the end of the. Interest receivable is an asset that arises when a company.
See The Accounting Treatment, The Balance Sheet Position, And The.
Web how you create an accrued interest journal entry depends on whether you’re the borrower or lender. Web the bank transaction journal entries below act as a quick reference, and set out the most commonly encountered situations when dealing with the double entry posting of banking. Web learn how to record interest receivable, the amount of interest earned but not yet collected, in a journal entry. When interest is accrued but not yet collected, it is recorded as.