How Are Credits Distinguished From Debits In The Journal - Web the total of the amount (s) entered as debits must equal the total of the amount (s) entered as credits. The two sides of the account show the pluses and minuses in the account. To use that same example from above, if you received that $5,000 loan, you would record a credit of. Web debits and credits are the opposing sides of an accounting journal entry. Web balance/ define debit and credit. So the cash would also have 50,000, but. Credit accounts are liabilities, equity and revenues. Web how are credits distinguished from debits in the journal? Web what’s the difference between debits and credits? Debits are dollar amounts that accountants post to the left side of the journal entry, and credits are dollar amounts.
3 Journal Entries Introduction Rules of Debit and Credit How to
Accounting uses debits and credits instead of negative numbers. This means that when you make. Debit is defined as “a record of indebtedness.” it is.
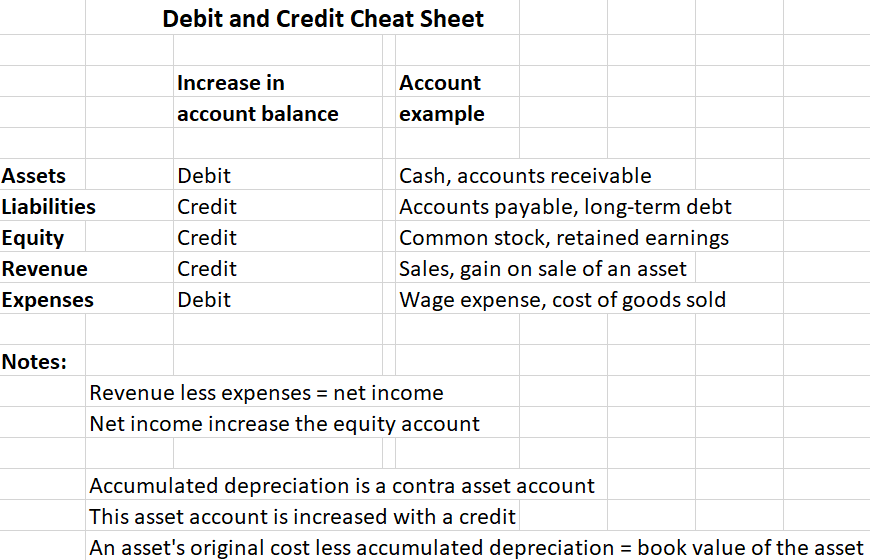
Debits and credits cheat sheet used in bookkeeping doubleentry
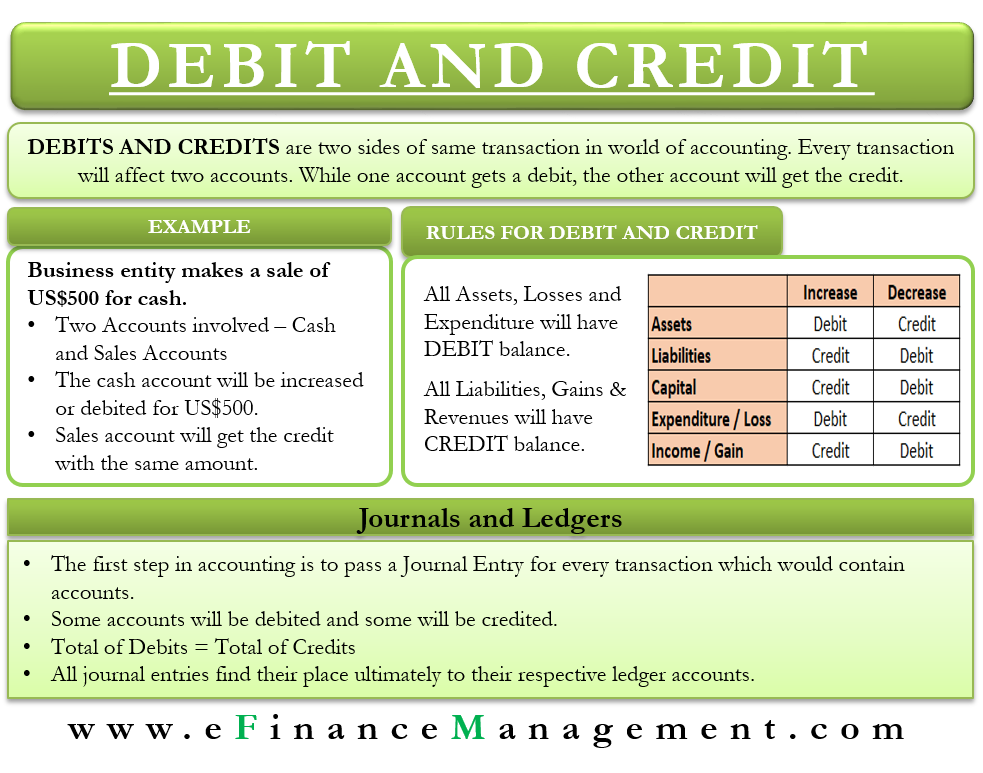
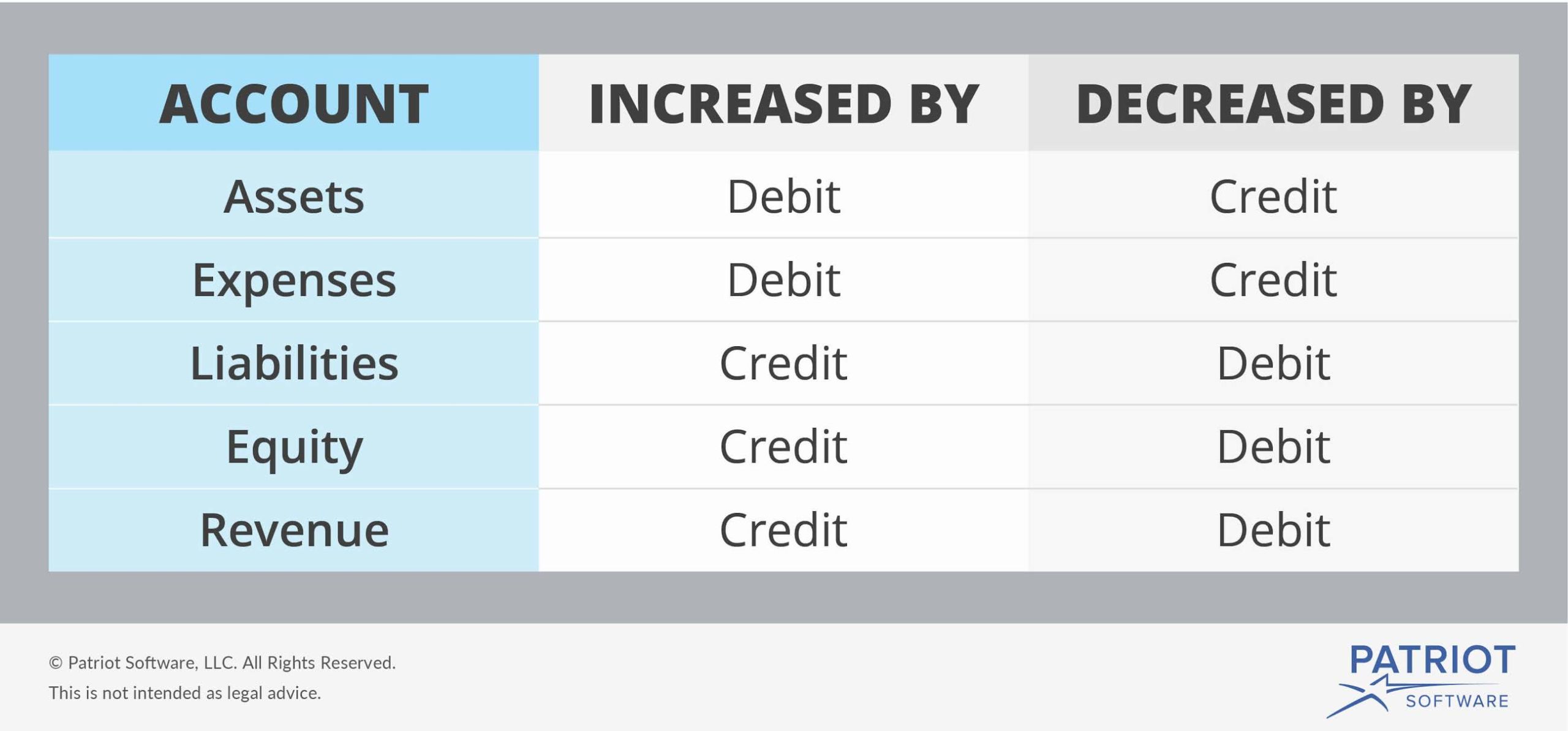
Debits increase assets and expenses, while credits increase. The two sides of the account show the pluses and minuses in the account. Web journal entries.
Printable Debits And Credits Cheat Sheet
Web debits and credits are traditionally distinguished by writing the transfer amounts in separate columns of an account book. Credit accounts are liabilities, equity and.
Accounting Debits And Credits Chart
When cash is received, debit cash. Web debit accounts are assets and expenses. You can think of “debit” as “ debit to get ” for.
Debits and Credits Introduction, Journal and ledger, Usage
This practice simplified the manual calculation of. Credits (cr) record money that flows out of an account. Web debits represent all transactions that reduce an.
Debits and Credits Cheat Sheet • 365 Financial Analyst
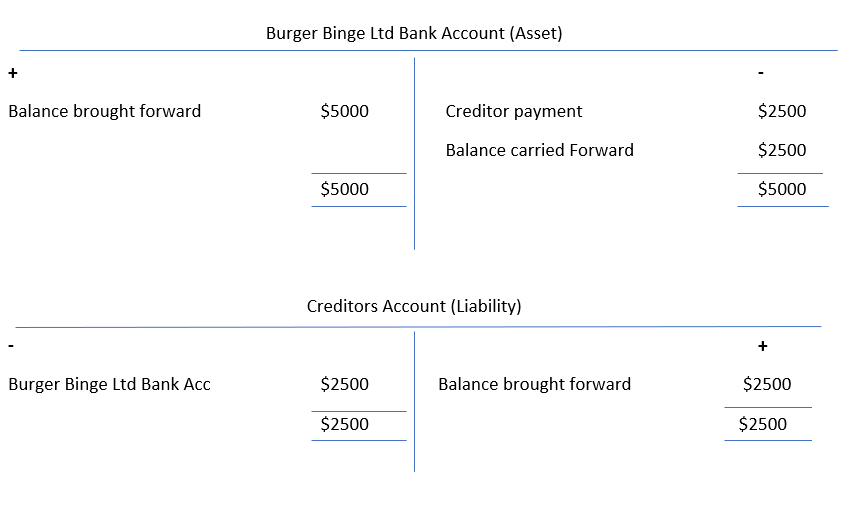
Web debits represent all transactions that reduce an account balance while credits represent those that increase it. When cash is paid out, credit. The difference.
Debits and Credits Cheat Sheet 365 Financial Analyst
The increase in assets and expenses are recorded on the debit. Debits are dollar amounts that accountants post to the left side of the journal.
Debits and Credits Accounting Play
Web debits and credits are the opposing sides of an accounting journal entry. To use that same example from above, if you received that $5,000.
Accounting Basics Part 1 Accrual DoubleEntry Accounting Debits
When we have the indentation, we're also going to invent the number into a separate column over here. Web debits and credits affect accounts differently.
Web So That Signifies That It's A Credit.
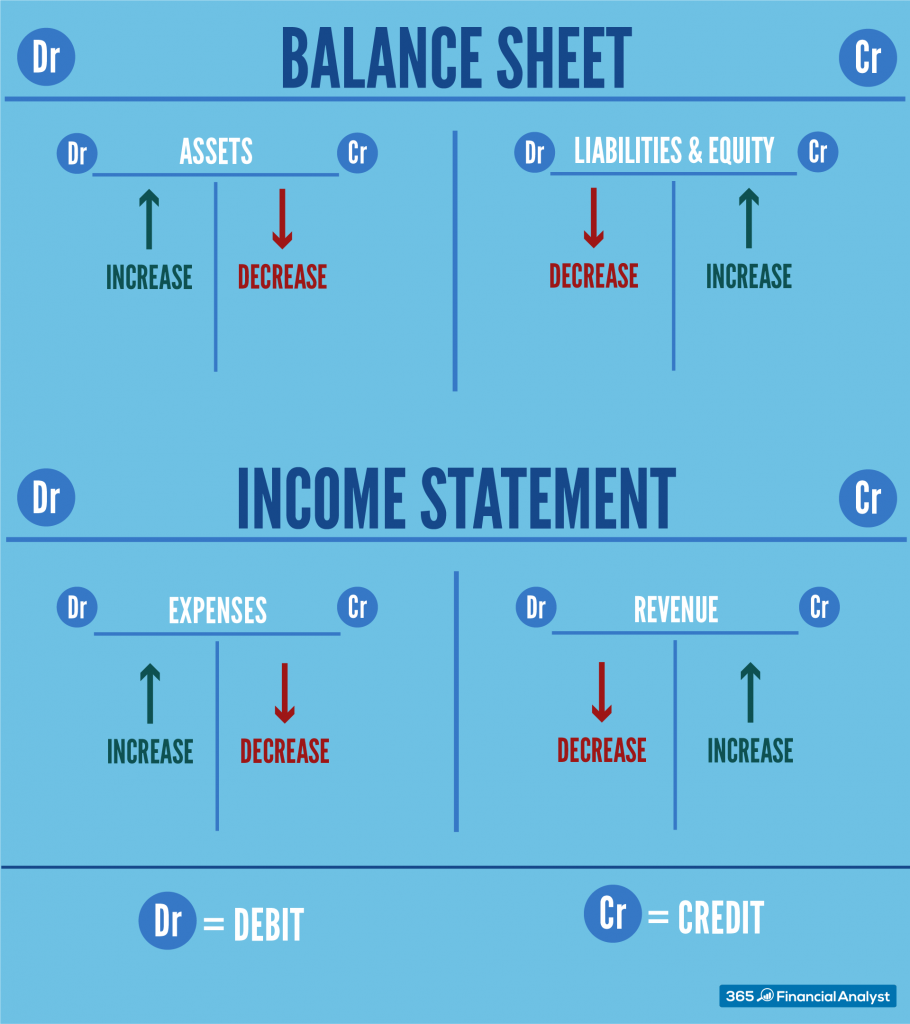
Debits increase assets and expenses, while credits increase. Web debits and credits affect accounts differently depending on their type: Journal entries must always balance out so that the total debit. When we have the indentation, we're also going to invent the number into a separate column over here.
Credit Accounts Are Liabilities, Equity And Revenues.
Web here is a sample account: When cash is received, debit cash. Web hence, based on the explanations, it is valid to say that in the journal, credits are distinguished from debits through indenting. Web a debit transaction refers to an increase in assets and expenses, while a credit transaction represents a decrease in these accounts.
This Practice Simplified The Manual Calculation Of.
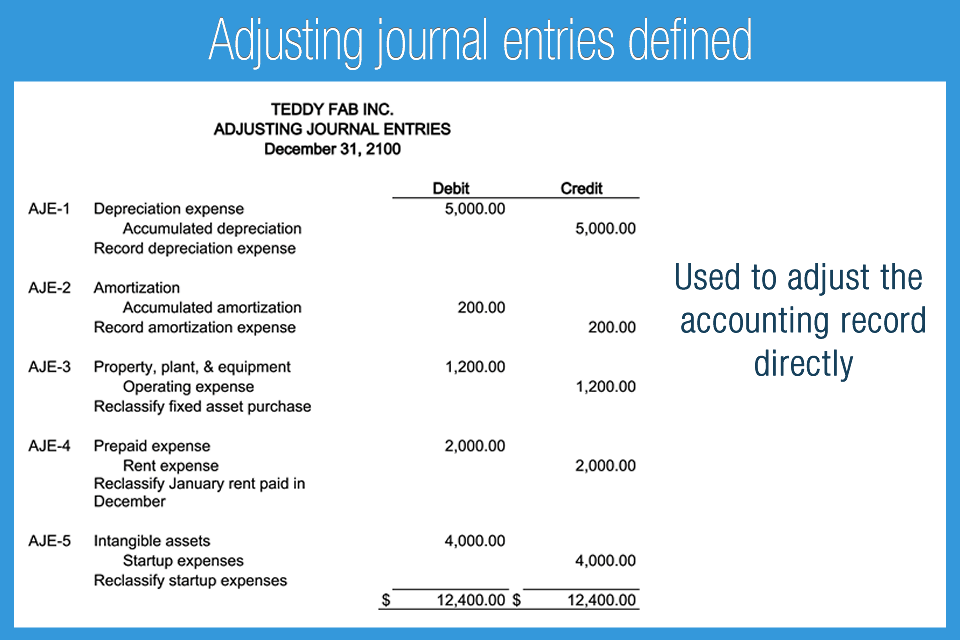
Web each general journal entry lists the date, the account title (s) to be debited and the corresponding amount (s) followed by the account title (s) to be credited and the. A debit typically increases asset and expense accounts and decreases liability, equity, and revenue accounts. Web journal entries consist of two sides: Web debit accounts are assets and expenses.
They Are Used To Change The Ending Balances In The General Ledger Accounts When.
How are credits distinguished from debits in the journal?a. A) indenting b) a line separation c) a different color d) there is no distinction You can think of “debit” as “ debit to get ” for assets and. Web balance/ define debit and credit.


/T-Account_2-cf96e42686cc4a028f0e586995b45431.png)